Molecular genetic structures such as a nucleus and a nucleoid are responsible for the incorporation of genetic information into genetic material. They are both sections of a live organism that are in charge of controlling inheritance as well as cellular processes. They also share the same genetic material, which is DNA. Despite the fact that the Nucleus and the Nucleoid have certain characteristics, they are vastly different from one another.
Nucleus Vs. Nucleoid
The most significant distinction between the Nucleus and the Nucleoid is that the Nucleus is a cell organelle that is responsible for storing and housing the genetic material of eukaryotic cells in the DNA, whereas the Nucleoid is responsible for storing and housing the genetic material of prokaryotic cells in the cytoplasm.
Among the many membrane-bound cell organelles found inside a eukaryotic cell, the nucleus is the most extensive and most important. The nucleus of eukaryotic cells is responsible for storing and protecting the genetic material of the cells. The nucleus of the cell is big and includes a significant number of chromosomes. Hepatocytes have an organelle that is well-organized, spherical in form and is enclosed by a double-layer membrane known as the nuclear membrane. The majority of the Nucleus is made up of DNA, RNA, enzymes, dissolved ions, and other subnuclear entities.
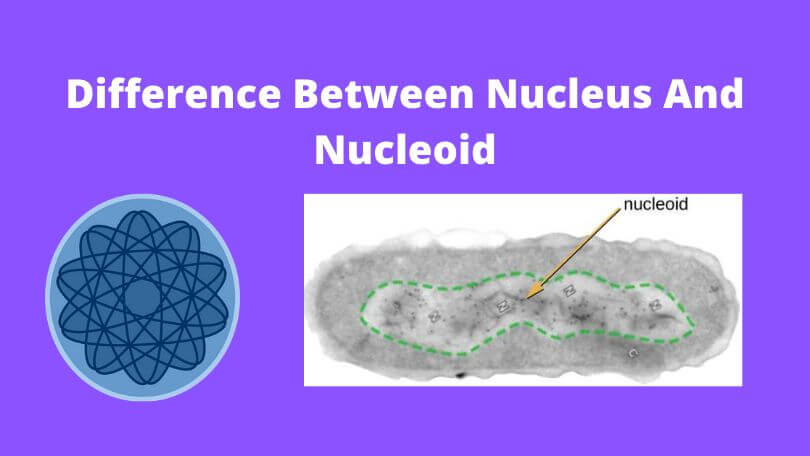
The Nucleoid is the name given to the irregularly shaped portion of a prokaryotic cell that contains the genetic material of the cell. The Nucleoid is responsible for storing and maintaining the genetic material of prokaryotes in their cytoplasm. The nucleoid is a tiny structure that houses just one chromosome. It is a poorly structured, irregularly shaped organelle that is devoid of a protective barrier, which makes it vulnerable to infection. The majority of a Nucleoid is made up of DNA, RNA, enzymes, and other proteins.
What is a Nucleus?
Among the many membrane-bound cell organelles found inside a eukaryotic cell, the nucleus is the most extensive and most important. The nucleus of eukaryotic cells is responsible for storing and protecting the genetic material of the cells.
In the cell, it is isolated from the other organelles by a nuclear membrane that is made up of two layers. The majority of the Nucleus is made up of DNA, RNA, enzymes, dissolved ions, and other subnuclear entities.
The Nucleus, which is spherical in form and includes multiple chromosomes, is a massive structure. It also possesses a well-organized nucleoplasm and nucleolus, which are both present. The nucleus is responsible for coordinating cellular processes such as growth and reproduction.
What is a Nucleoid?
The Nucleoid is the name given to the irregularly shaped portion of a prokaryotic cell that contains the genetic material of the cell. The Nucleoid is responsible for storing and maintaining the genetic material of prokaryotes in their cytoplasm.
The nucleoid does not have a protective membrane around it. Therefore, it is not distinguished from the other prokaryotic constituents of the organism. The majority of a Nucleoid is made up of DNA, RNA, enzymes, and other proteins. In addition, they include a single chromosome, which is the circular DNA molecule, which makes them uneven and irregular in form.
The Nucleoid is an irregular-shaped structure that is poorly structured and tiny in size. When looking at a Nucleoid, you will see that it is devoid of Nucleoplasm and Nucleolus.
Difference between a nucleus and a nucleoid
- In eukaryotic cells, the Nucleus is the most widespread and most important membrane-bound cell organelle, but in prokaryotic cells, the Nucleoid is the irregularly shaped area carrying the genetic material.
- The Nucleus is responsible for storing and housing the genetic material of eukaryotic cells, while the Nucleoid is responsible for storing and housing the genetic material of prokaryotic cells in the cytoplasm.
- The nucleus has a spherical form, but the nucleoid has an irregular and uneven shape, as seen in Figure
- In contrast to the nucleus, the nucleoid is composed of a single chromosome, that is, the circular DNA molecule, which is found in the nucleus.
- A two-layer nuclear membrane surrounds the nucleus, but the nucleoid does not have a protective barrier around it.
- In contrast to nucleoids, which are tiny and ill-organized, the nucleus is massive and very well-organized.
- the nucleus is isolated from the other organelles in the cell by a nuclear membrane that is double-layered in structure. Nucleoid, on the other hand, does not have a protective membrane around it. Therefore, it is not distinguished from the other prokaryotic constituents of the organism.
Conclusion
Molecular genetic structures such as a nucleus and a nucleoid are responsible for the incorporation of genetic information into genetic material. They are both sections of a live organism that are in charge of controlling inheritance as well as cellular processes. They also share the same genetic material, which is DNA. Despite the fact that the Nucleus and the Nucleoid have certain characteristics, they are vastly different from one another.
Among the many membrane-bound cell organelles found inside a eukaryotic cell, the nucleus is the most extensive and most important. The nucleus of the cell is big and includes a significant number of chromosomes. It is a spherically shaped organelle with a well-organized structure. The nucleus is isolated from the other organelles in the eukaryotic cell by a double-layered nuclear membrane that serves as a physical barrier.
The Nucleoid is the name given to the irregularly shaped portion of a prokaryotic cell that contains the genetic material of the cell. The Nucleoid is a tiny chromosome that includes a single circular DNA molecule. It is found on a single chromosome. It is a poorly structured, irregularly shaped organelle that is devoid of a protective barrier, which makes it vulnerable to infection. Therefore, it is not distinguished from the other prokaryotic constituents of the organism.
The most significant distinction between a Nucleus and a Nucleoid is that they serve distinct tasks and perform distinct functions. While the Nucleus of a eukaryotic cell is responsible for storing and homing the genetic material of the cell, the Nucleoid of a prokaryotic cell is responsible for storing and homing the genetic material of the cell in the cytoplasm.